Appearance
Classpath And Jar
In Java, we often hear about classpath . There are many articles on the Internet about "how to set classpath", but most of the settings are unreliable.
What exactly is classpath ?
classpath is an environment variable used by the JVM to instruct the JVM how to search for class .
Because Java is a compiled language, the source code file is .java , and the compiled .class file is the bytecode that can actually be executed by the JVM. Therefore, the JVM needs to know where to search for the corresponding Hello.class file if it wants to load a class abc.xyz.Hello .
Therefore, classpath is a collection of directories, and the search path it sets is related to the operating system. For example, on a Windows system, separated by ; and directories with spaces enclosed in "" , it may look like this:
sh
C:\work\project1\bin;C:\shared;"D:\My Documents\project1\bin"On a Linux system, separated by : , it may look like this:
sh
/usr/shared:/usr/local/bin:/home/yourname/binNow we assume that classpath is .;C:\work\project1\bin;C:\shared , when the JVM loads the abc.xyz.Hello class, it will look for:
<Current directory>\abc\xyz\Hello.classC:\work\project1\bin\abc\xyz\Hello.classC:\shared\abc\xyz\Hello.class
Note that . represents the current directory. If the JVM finds the corresponding class file in a certain path, it will not continue searching further. If it is not found in all paths, an error will be reported.
There are two ways to set classpath :
- Setting the
classpathenvironment variable in the system environment variable is not recommended; - Setting the
classpathvariable when starting the JVM is recommended.
We strongly do not recommend setting classpath in the system environment variable, as it will pollute the entire system environment. It is recommended to set classpath when starting the JVM. In fact, the -classpath parameter is passed to the java command:
sh
java -classpath .;C:\work\project1\bin;C:\shared abc.xyz.HelloOr use the -cp abbreviation:
sh
java -cp .;C:\work\project1\bin;C:\shared abc.xyz.HelloIf the system environment variable is not set and the -cp parameter is not passed in, the default classpath of the JVM is . , which is the current directory:
sh
java abc.xyz.HelloThe above command tells the JVM to search for Hello.class only in the current directory.
When running a Java program in the IDE, the -cp parameter automatically passed in by the IDE is the bin directory of the current project and the introduced jar package.
Usually, in class we write, we will reference class of the Java core library, such as String , ArrayList , etc. Where should I find these class ?
There are many "how to set classpath" articles that will tell you to put rt.jar that comes with the JVM into classpath , but in fact, there is no need to tell the JVM how to find class in the Java core library. How can the JVM be so stupid that it can't even install its own core?
Notice
Do not add any Java core libraries to the classpath! The JVM does not rely on classpath to load core libraries at all!
Better yet, don't set classpath ! The default current . is sufficient for most situations.
Suppose we have a compiled Hello.class , its package name is com.example , and the current directory is C:\work . Then, the directory structure must be as follows:
C:\work
└─ com
└─ example
└─ Hello.classTo run this Hello.class you must use the following command in the current directory:
sh
C:\work> java -cp . com.example.HelloThe JVM searches for com.example.Hello in the current directory based on the classpath . , that is, the actual search file must be located at com/example/Hello.class . If the specified .class file does not exist, or the directory structure and package name do not match, an error will be reported.
jar package
If there are many .class files scattered in various directories, it will definitely be difficult to manage. It would be much more convenient if the directory could be packaged and turned into a file.
The jar package is used to do this. It can convert the directory hierarchy of package organization and all the files in each directory (including .class files and other files) into a jar file. In this way, whether it is backup, It’s much easier to just send it to the customer.
The jar package is actually a compressed file in zip format, and the jar package is equivalent to a directory. If we want to execute a class in a jar package, we can put the jar package in classpath :
sh
java -cp ./hello.jar abc.xyz.HelloIn this way, the JVM will automatically search for a certain class in the hello.jar file.
So the question is: how to create a jar package?
Because the jar package is a zip package, you can directly find the correct directory in the resource manager, right-click, and select "Send to" and "Compressed (zipped) folder" in the pop-up shortcut menu to create a zip document. Then, change the suffix from .zip to .jar , and a jar package will be created successfully.
Assume that the directory structure of the compilation output is as follows:
package_sample
└─ bin
├─ hong
│ └─ Person.class
│ ming
│ └─ Person.class
└─ mr
└─ jun
└─ Arrays.classWhat needs special attention here is that the first-level directory in the jar package cannot be bin , but should be hong , ming , or mr . If you look at it in Windows Explorer, it should look like this:
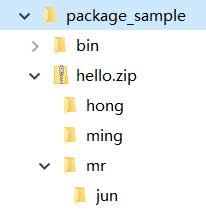
If it looks like this:
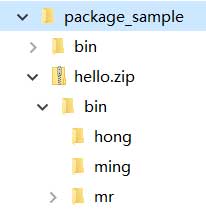
The above hello.zip contains the bin directory, indicating that there is a problem with the packaging. The JVM still cannot find the correct class from the jar package. The reason is that hong.Person must be stored as hong/Person.class , not bin/hong/Person.class .
The jar package can also contain a special /META-INF/MANIFEST.MF file. MANIFEST.MF is plain text and can specify Main-Class and other information. The JVM will automatically read this MANIFEST.MF file. If Main-Class exists, we do not have to specify the startup class name on the command line, but use a more convenient command:
sh
java -jar hello.jarIn large projects, it is impossible to manually write the MANIFEST.MF file and then manually create the jar package. The Java community provides a large number of open source build tools, such as Maven , which can easily create jar packages.
Summary
The JVM determines the path and order of searching for class through the environment variable classpath ;
It is strongly recommended not to set the system environment variable classpath . It is recommended to always pass it through the -cp command;
The jar package is essentially in zip format, which is equivalent to a directory and can contain many .class files for easy downloading and use;
The MANIFEST.MF file can provide information about the jar package, such as Main-Class , so that the jar package can be run directly.